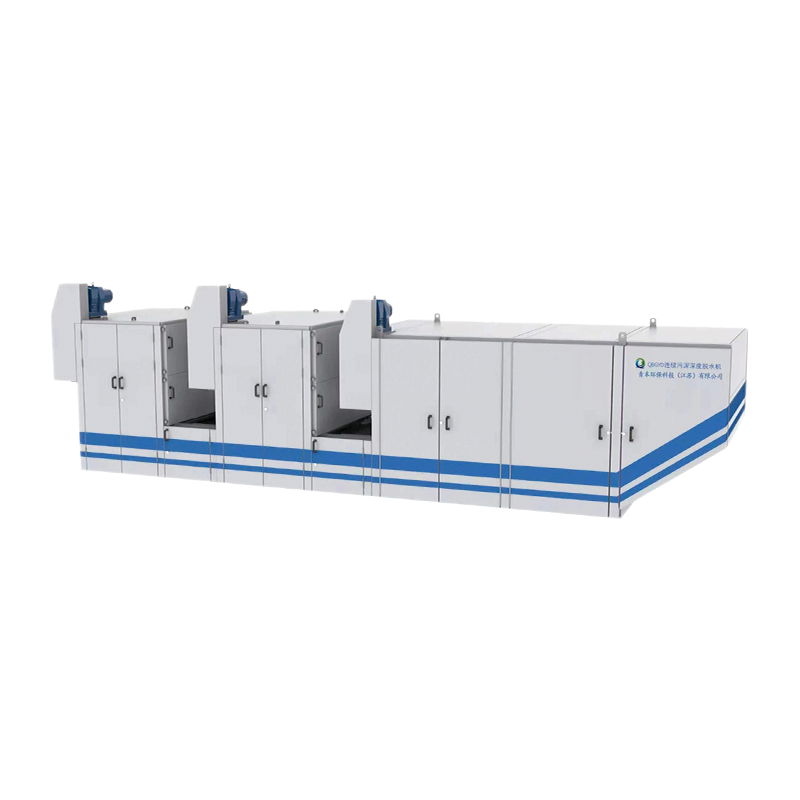
Content
1. 3 factors affecting the accuracy of integrated dosing devices
Before optimization, you need to understand which factors will cause dosing fluctuations:
Stability of metering pumps
Pump wear, pulsation or calibration deviation will cause flow errors.
The accuracy of low-quality metering pumps will drop significantly after long-term operation.
Sensor and control system errors
pH/ORP sensor drift, flow meter data is inaccurate.
PLC or PID control parameters are not optimized, and the response is delayed.
Reagent characteristics and pipeline problems
High-viscosity agents are prone to uneven pumping or pipeline crystallization blockage.
Pipeline leakage or back pressure changes affect the actual dosage.
2. 3 key methods to improve dosing accuracy
- Method 1: Calibrate metering pumps and sensors
Operation steps:
Regularly calibrate metering pumps:
Use a standard measuring cylinder to measure the output flow, compare with the set value, and adjust the stroke or frequency.
It is recommended to calibrate once a month, and the industry with high precision requirements can be shortened to weekly.
Verify sensor data:
pH/ORP electrodes need to be calibrated with standard buffer (such as pH4.0/7.0/9.2).
The flowmeter can be verified by ultrasonic flowmeter comparison.
- Method 2: Optimize control system parameters
Key adjustment items:
PID parameter setting:
Proportional band (P): Reducing it can speed up the response, but excessive will cause oscillation.
Integral time (I): Eliminate static errors, but setting it too long will delay adjustment.
Derivative time (D): Suppress overshoot and is suitable for systems with large lag.
Adopt adaptive control algorithm:
For scenarios with large water quality fluctuations (such as sewage treatment), fuzzy control or model predictive control (MPC) can be used.
Tool recommendation:
Use the self-tuning function of PLC or DCS system.
- Method 3: Improve the design of pharmaceutical delivery pipeline
Optimization plan:
Reduce pipeline resistance:
Shorten the pipeline length, avoid right-angle elbows, and use large curvature radius elbows instead.
High-viscosity pharmaceuticals require large-diameter pipelines (DN≥25mm).
Prevent crystallization/bubble interference:
Install a flushing water device in the pipeline of easily crystallized reagents (such as citric acid).
Set an exhaust valve at the high point of the pipeline to prevent air blockage from affecting the flow rate.
Choose the right material:
Use PVDF or 316L stainless steel pipes for corrosive reagents (such as sodium hypochlorite).
3. A Guide to Safety, Maintenance and Optimization of Integrated Dosing Plants
Safety operation specifications
Check before starting
Confirm that the power supply voltage is consistent with the equipment requirements (380V/220V)
Check the liquid level of the storage tank to avoid dry operation and damage to the pump body
Verify the status of the pipeline valve (inlet open/outlet open/exhaust valve closed)
Chemical safety
Corrosive chemicals (such as hydrochloric acid, sodium hypochlorite):
Wear anti-corrosion gloves and goggles during operation
Anti-leak alarms and emergency flushing devices must be installed in the dosing room
Flammable chemicals (such as methanol):
It is prohibited to use open flames or non-explosion-proof electrical appliances in the dosing area
The storage tank must be grounded to prevent static electricity
Emergency treatment
Stop the machine immediately if a leak is found, and close the inlet and outlet valves
In case of electrical failure, cut off the power supply before repair
Prevention of common problems
Inaccurate dosage
Possible causes:
Damage to the metering pump diaphragm
Improper adjustment of the back pressure valve
Sensor data drift
Solution:
Calibrate the pump and sensor according to the previous method
Install a pressure gauge to monitor the pipeline back pressure (it is advisable to maintain 0.2-0.3MPa)
Abnormal pump noise
Cavitation sound → Check whether the inlet filter is blocked
Mechanical friction sound → Check the lubrication of the connecting rod bearing
Control system alarm
"Low liquid level" alarm: Check the float switch or capacitive liquid level gauge
"Overload" alarm: Verify whether the motor current exceeds the limit
4. Integrated dosing device FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What should be noted during installation?
The pipeline should be short, avoid right-angle bends, and reduce resistance.
A Y-type filter (gap 0.3mm) should be installed at the inlet of the reagent to prevent clogging by impurities.
The electrical wiring must meet the explosion-proof requirements, and the corrosive environment must be sealed.
- How to solve the abnormal liquid suction of the metering pump?
Check whether the inlet pipeline is blocked or leaking, and tighten the connection.
Adjust the stroke to 100% and ensure that the drainage holes on the back plate are aligned.
When the pulse width is insufficient, it can be extended to 300ms to improve stability.
- Common faults and solutions:
|
Fault phenomenon |
Possible causes |
Solutions |
|
Unstable flow |
Inlet pipe blocked/gas entering |
Clean filter, exhaust |
|
Safety valve frequently trips |
Improper spring pressure setting/system overpressure |
Adjust spring or check pressure setting |
|
Abnormal pump noise |
Diaphragm damage/hydraulic oil contamination |
Replace diaphragm or hydraulic oil |