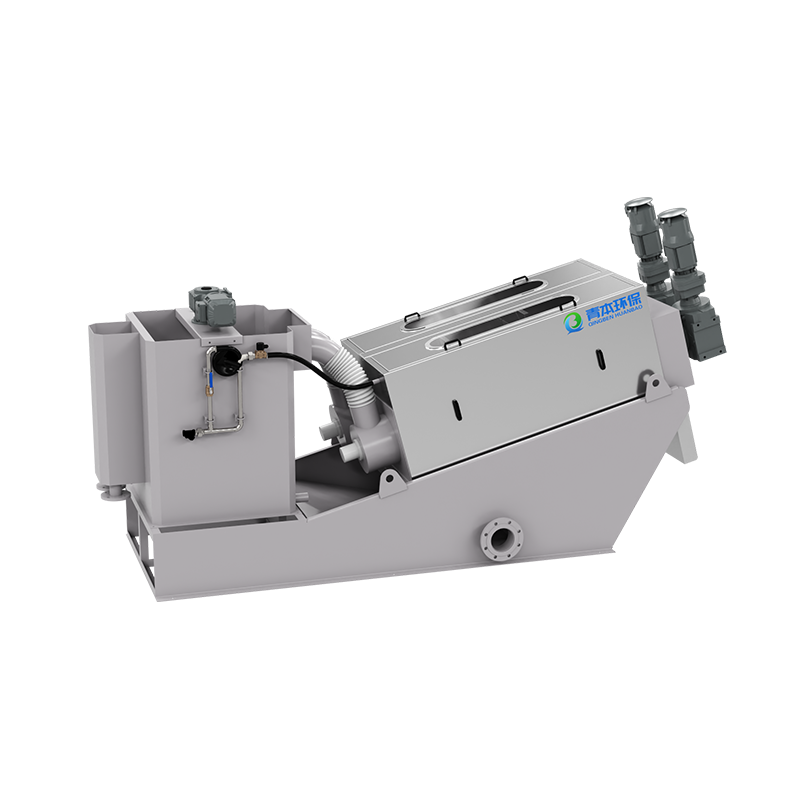
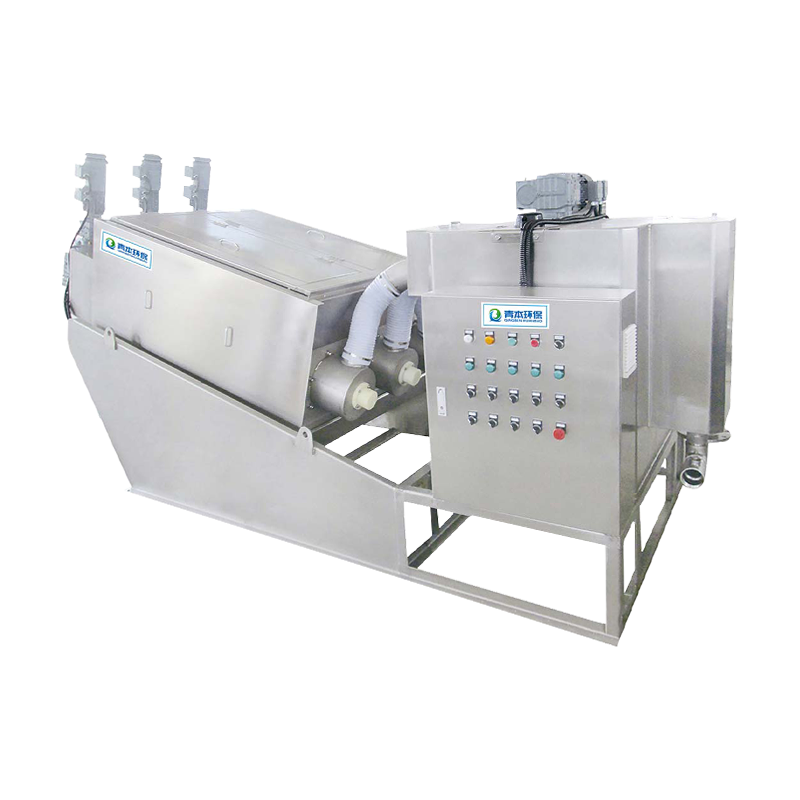
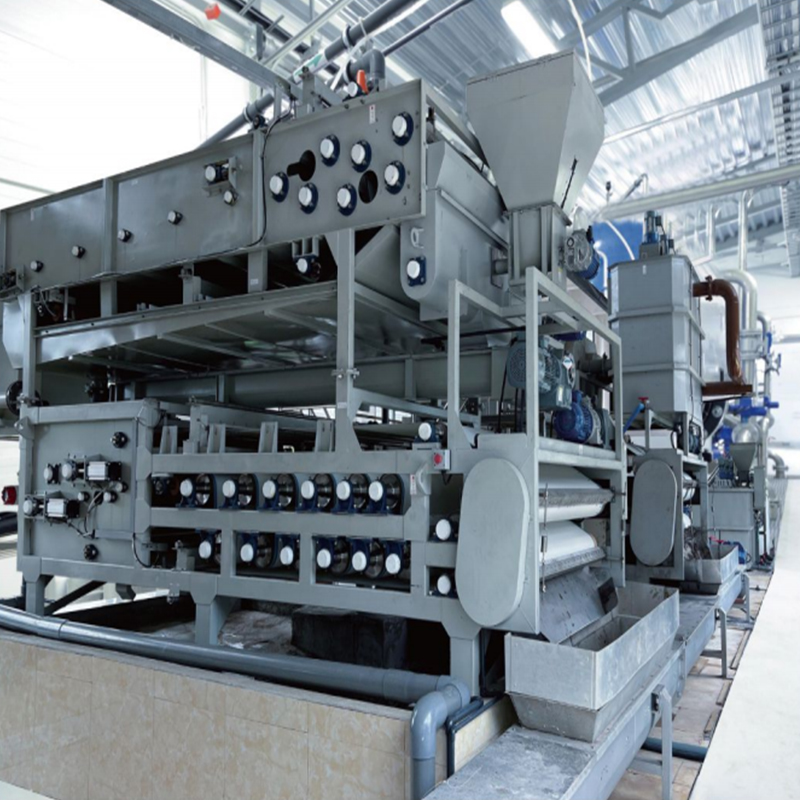
1. The role of high pressure belt continuous sludge dewatering machine in sewage treatment
In the sewage treatment process, sludge dewatering is a crucial link. Traditional dewatering equipment often has problems such as low dewatering efficiency, high energy consumption, and limited processing capacity. The emergence of high pressure belt continuous sludge deep dewatering machine effectively solves these problems and plays an irreplaceable role in sewage treatment:
Significantly improve dewatering efficiency: High pressure belt continuous sludge deep dewatering machine can reduce the sludge moisture content from 98%-99% to below 60% at one time, greatly reduce the sludge volume, and achieve sludge reduction
Continuous automatic operation: The machine adopts a continuous belt design, which can achieve 24-hour uninterrupted operation, and the processing capacity can reach 2-3 times that of traditional equipment
Reduce processing costs: Compared with traditional centrifugal dewatering machines, energy consumption Reduce by 30%-40%, save a lot of operating expenses, and reduce costs
Improve resource recovery rate: the calorific value of the mud cake after dehydration is increased, which is more conducive to subsequent incineration power generation or composting
Reduce secondary pollution: the closed design effectively controls the spread of odor and improves the working environment
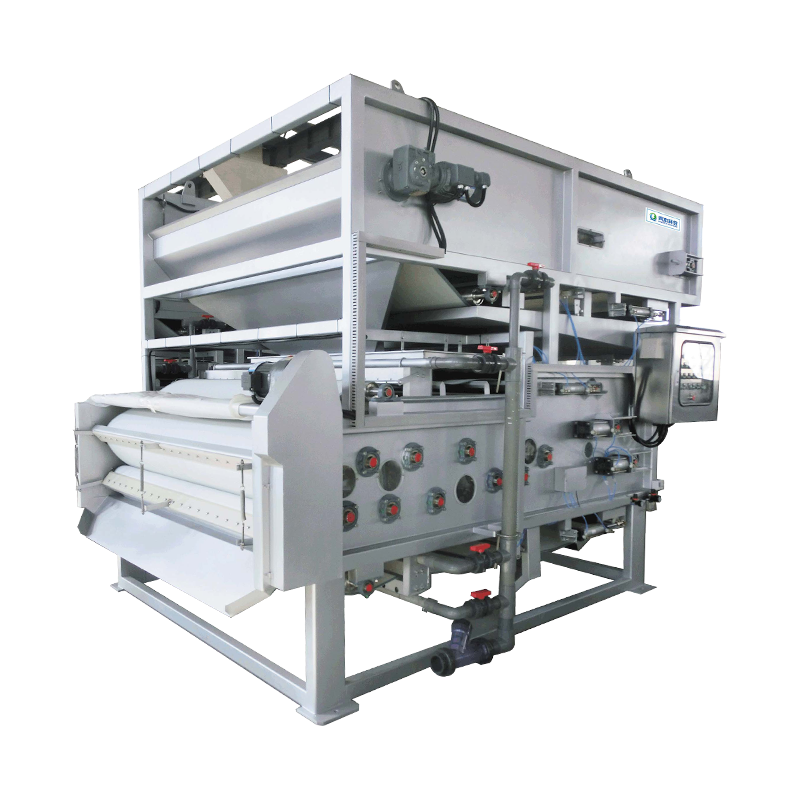
2. Working principle: perfect combination of triple dehydration mechanisms
The excellent performance of the high-pressure belt continuous sludge deep dehydrator comes from its unique working principle. It cleverly combines the three mechanisms of gravity dehydration, wedge pressing and high-pressure dehydration to form an efficient dehydration system.
- First stage: gravity dehydration zone
The chemically conditioned sludge is first evenly distributed on the moving filter belt. Under the action of gravity, a large amount of free water naturally seeps out through the gaps between the filter belts. This stage can remove about 50% of the water in the sludge, laying the foundation for subsequent deep dehydration.
- Second stage: wedge pre-pressing zone
The sludge then enters the gradually narrowing wedge area and is subjected to slowly increasing pressure. The special filter belt structure and arrangement design make the sludge evenly squeezed, further releasing the bound water. The pressure at this stage is usually controlled at 0.1-0.3MPa.
- The third stage: high-pressure dehydration zone
This is the core part of the equipment. The sludge enters the "S"-shaped pressing zone composed of multiple high-pressure filter belts. Through the carefully designed roller system layout, a high pressure of 0.5-1.5MPa is applied to force the water out of the sludge particles. The uniqueness of the high-pressure zone lies in its progressive pressurization design, which avoids the problem of filter belt blockage caused by sudden high pressure.
During the entire dehydration process, the equipment is also equipped with an automatic deviation correction device, a filter belt washing system and an intelligent control system to ensure that the dehydration process is stable and efficient. Some high-pressure belt dehydrators use variable frequency speed regulation technology, which can adjust the operating parameters in real time according to the properties of the sludge to achieve intelligent operation.
3. Key points to note during use
Although the high-pressure belt continuous sludge deep dewatering machine has many advantages, to give full play to its performance, the following key points must be noted in actual use:
Sludge conditioning
Select appropriate flocculants (usually cationic PAM) according to the properties of the sludge
Control the optimal dosage (usually 0.1%-0.3% of the dry sludge amount)
Ensure that the flocculant and sludge are fully mixed to form a solid floc
Pay attention to adjusting the sludge pH value to the optimal range of 6-8
Operation parameter regulation
The filter belt tension should be maintained in an appropriate range (usually 0.3-0.5MPa)
Control the reasonable filter belt speed (usually 2-10m/min adjustable)
Adjust the feed rate according to the sludge concentration to avoid overload
Monitor the main motor current , ensure that it is within the rated range
Daily maintenance points
Clean the filter belt regularly (at least once per shift)
Check the sensitivity of the correction device to prevent the filter belt from running off
Add grease to the bearing on time
Monitor the wear of the filter belt and replace it in time
Maintain the flushing water pressure at 0.4-0.6MPa
Operation specifications
Do not touch the moving parts with your hands when the equipment is running
The power must be cut off and a warning sign must be hung during maintenance
Personal protection is required when handling toxic sludge
Press the emergency stop button immediately in an emergency
Handling of abnormal situations
Filter belt slips: Check the tensioning device and adjust the air pressure
Decrease in dehydration effect: Check the flocculant effect and whether the filter belt pores are blocked
Increase in equipment vibration: Check whether the roller bearing is damaged
Increase in sludge water content: Adjust pressure parameters or reduce processing volume