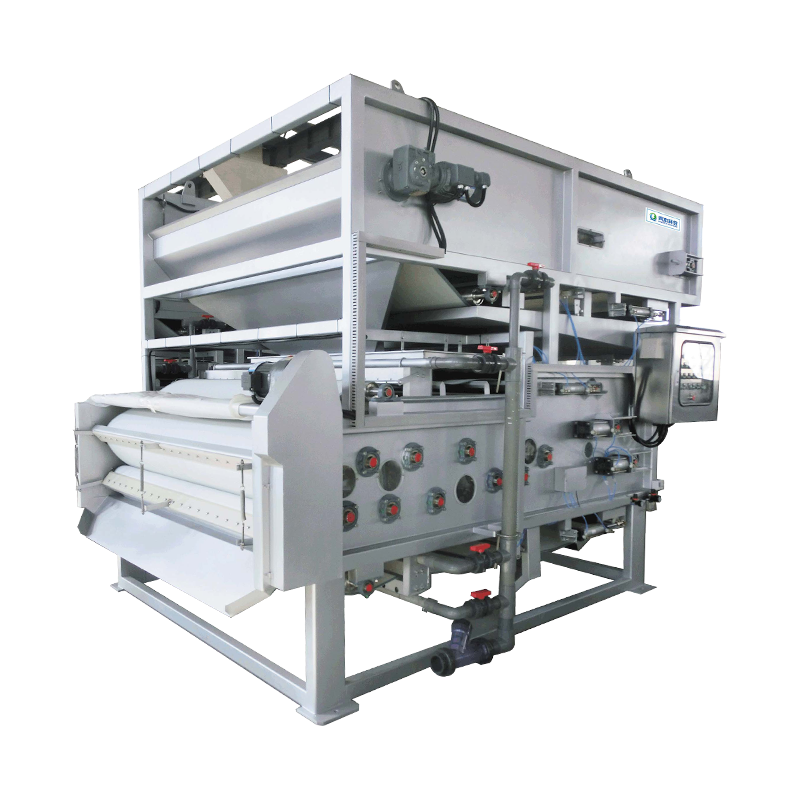
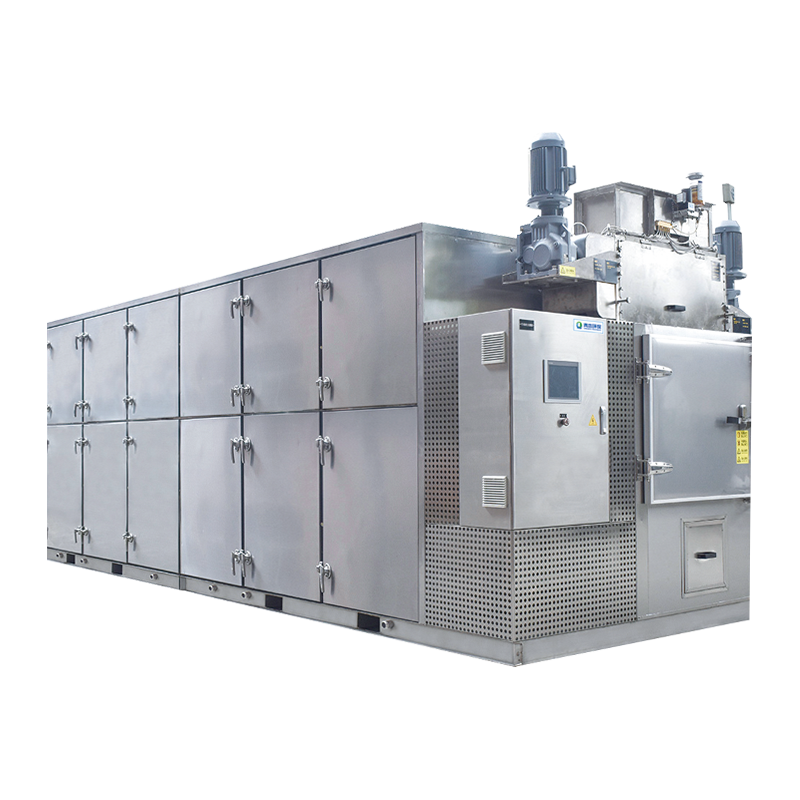
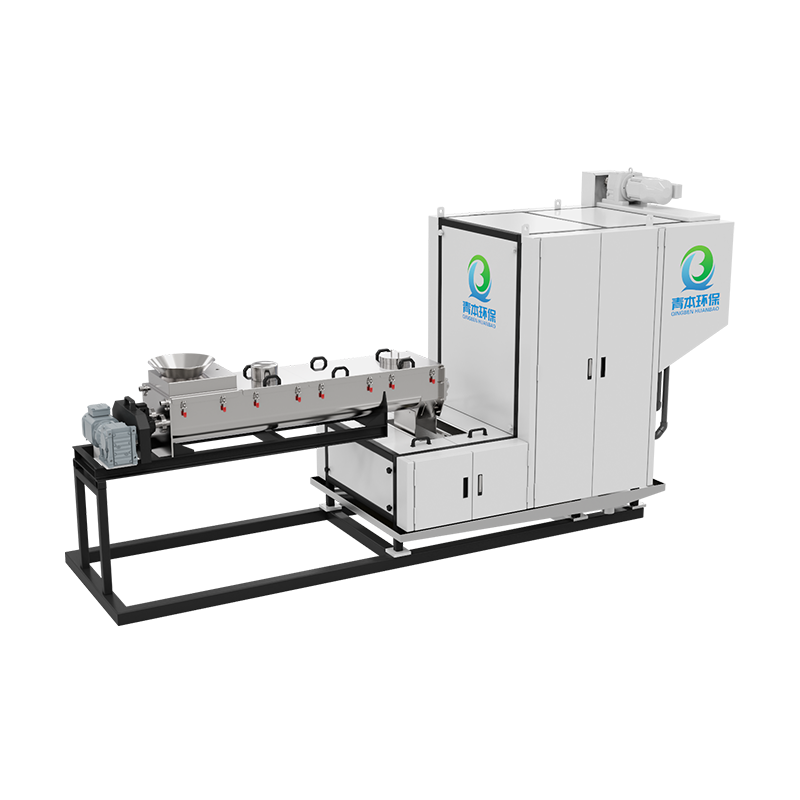
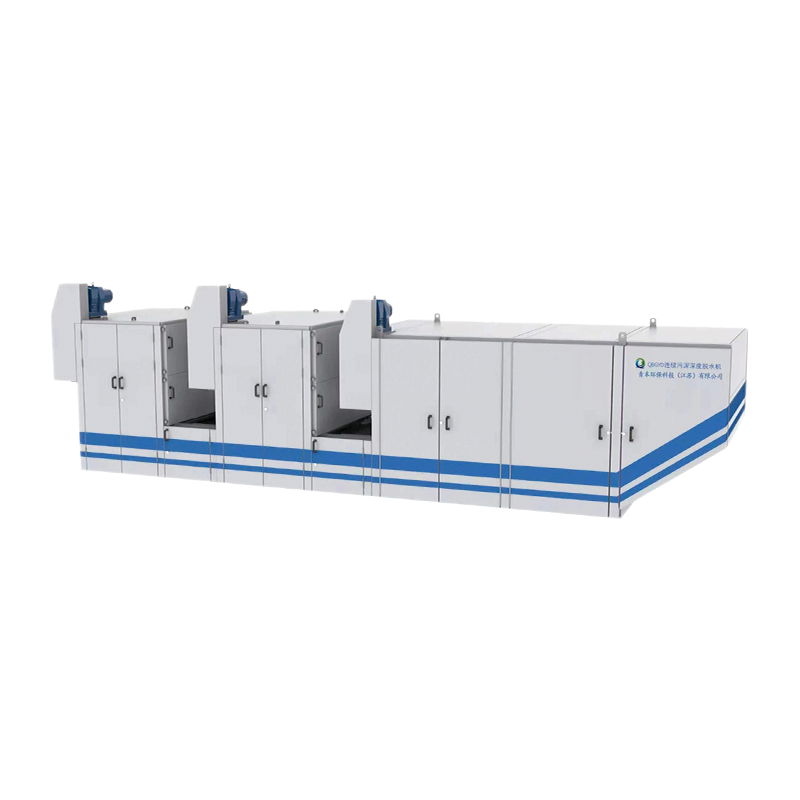
Selecting a suitable sludge cryogenic chamber dryer is a systematic process that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including sludge characteristics, treatment objectives, budget, and operating costs.
Step 1: Define the Work Requirements
This is the foundation for selecting the appropriate sludge cryogenic chamber dryer. You must clearly define your project requirements.
Sludge Property Analysis:
Source: Is it municipal sludge (domestic sewage) or industrial sludge (from printing and dyeing, papermaking, chemicals, food, etc.)? Industrial sludge has a more complex composition and may require specific equipment materials.
Physical Properties: Initial moisture content (usually around 80%), viscosity, oil content, and sand content. Highly viscous sludge may require special feed or distribution equipment.
Chemical Properties: pH, corrosiveness (chloride and sulfide content), organic matter content, and calorific value. This determines the corrosion resistance of the equipment material (such as 304 or 316L stainless steel).
Processing Scale:
Wet Sludge Processing Capacity: How many tons of wet sludge with an 80% moisture content need to be processed daily or hourly? This is the core parameter for determining equipment size.
Ultimate Goal (Dried Sludge Disposal):
Target Moisture Content: What moisture content do you want the dried sludge to have? (e.g., 40%, 30%, 10%). Different disposal options have different requirements:
Incineration: A moisture content of ≤30% is sufficient, which is a lower requirement.
Fertilizer/Soil Improvement: A moisture content of ≤30% is required, and low temperatures are required to preserve organic matter.
Building Material Utilization/Landfill: A moisture content of ≤40% or lower is required.
Sale as Fuel: A moisture content of ≤20% is required, which is the highest requirement and also results in the highest energy consumption.
Site Conditions:
Installation Location: Indoors or Outdoors? Is there sufficient space (length, width, and height)?
Utilities: Available power (voltage, power), steam source, water source, etc.
Step 2: Evaluate Key Technical Parameters
Based on the requirements from Step 1, evaluate the technical features of different suppliers and equipment. Drying Technology Principles:
Heat Pump (Closed Cycle): This is the current mainstream and most recommended technology. It uses a refrigerant compression-expansion cycle to recover the latent heat of water vapor in the exhaust air, resulting in a high energy efficiency ratio. Advantages include energy saving, environmental protection (minimal exhaust emissions), stable operation, and high safety. It is well-suited for municipal sludge and most industrial sludge.
Low-Temperature Flue Gas/Hot Water: This utilizes low-temperature waste heat (80-100°C flue gas or hot water) from power plants or incinerators as a heat source. Its advantages include extremely low operating costs, but it requires a stable, inexpensive, or free heat source and is relatively complex.
Drying Temperature and Safety:
Ensure the operating temperature is within the low-temperature range of 60-85°C. This is a key safety factor, completely eliminating the risk of sludge spontaneous combustion and dust explosions.
Inquire about the equipment's explosion-proof design (such as internal oxygen content control and anti-static measures) and inert gas protection system.
Equipment Materials and Corrosion Resistance:
Parts that come into contact with hot, moist sludge and corrosive gases must be made of stainless steel. Standard Configuration: Parts in contact with sludge are constructed of 304 stainless steel.
For highly corrosive industrial sludge, 316L stainless steel or higher-grade corrosion-resistant materials must be selected. This is critical to the equipment's durability and lifespan.
Automation Level:
Check the intelligence level of the control system. Good equipment should be capable of fully automatic operation, including:
One-touch start and stop.
Automatic Temperature and Humidity Adjustment: Automatically adjusts temperature, air volume, feed rate, and other parameters based on the set sludge moisture content.
Remote Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis: Supports remote monitoring via PC and mobile app, providing timely alarms.
Heat Source Selection:
Select the most economical heat source based on your specific conditions:
Electricity: Most commonly used, convenient but relatively expensive.
Steam: Low operating costs if an inexpensive steam source is available.
Natural gas: High calorific value, but requires additional burners and carries safety risks.
Waste heat: Most economical, but requires a stable source.