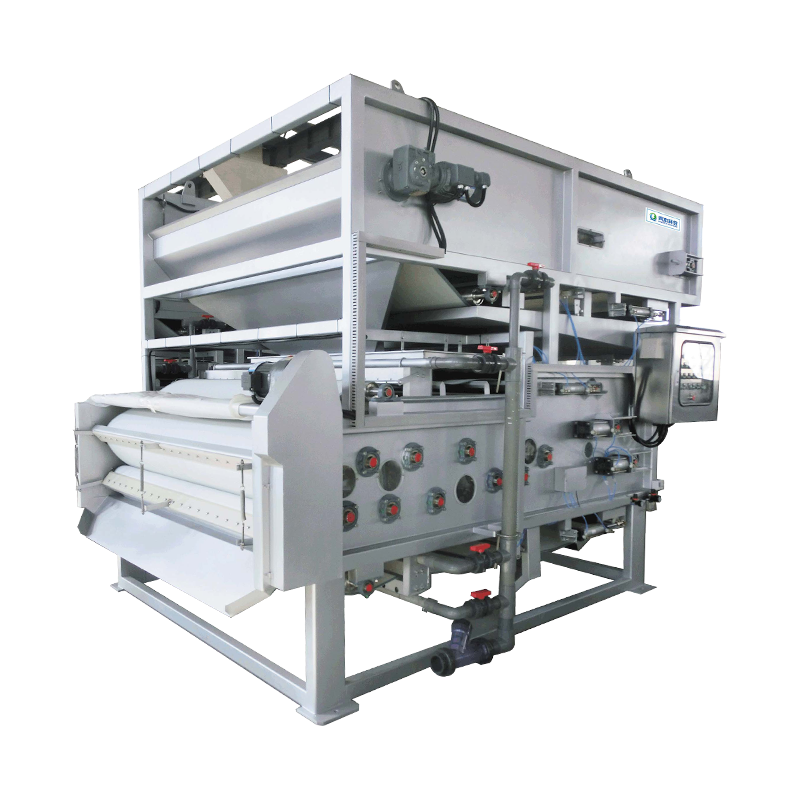
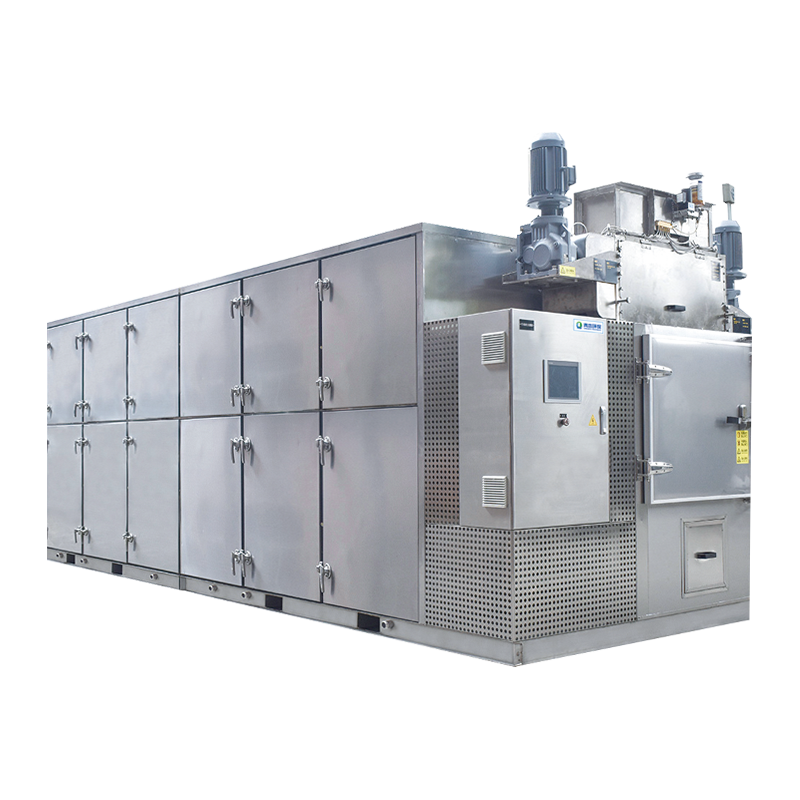
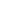
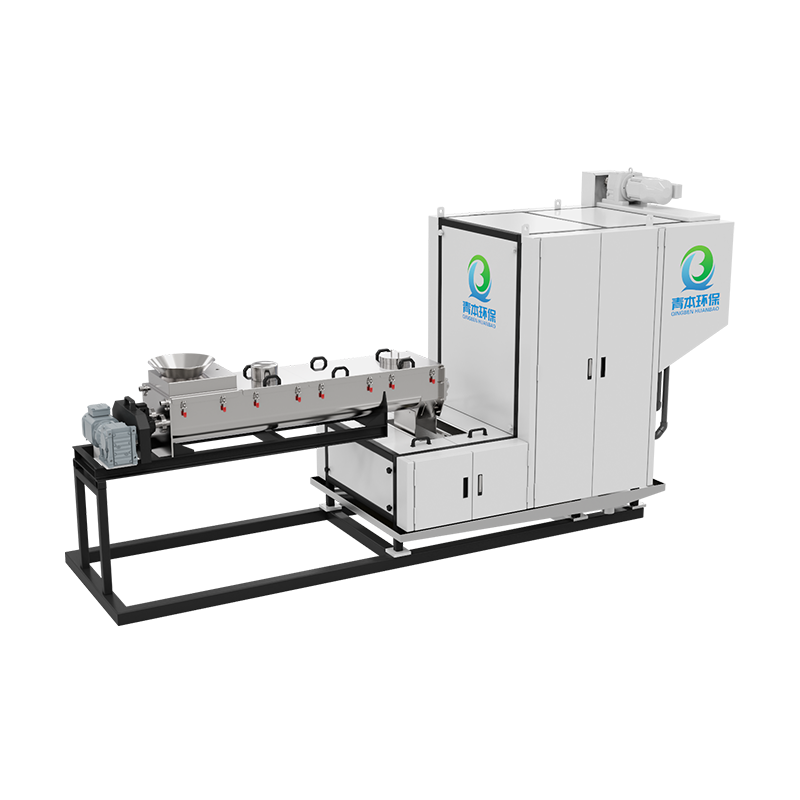
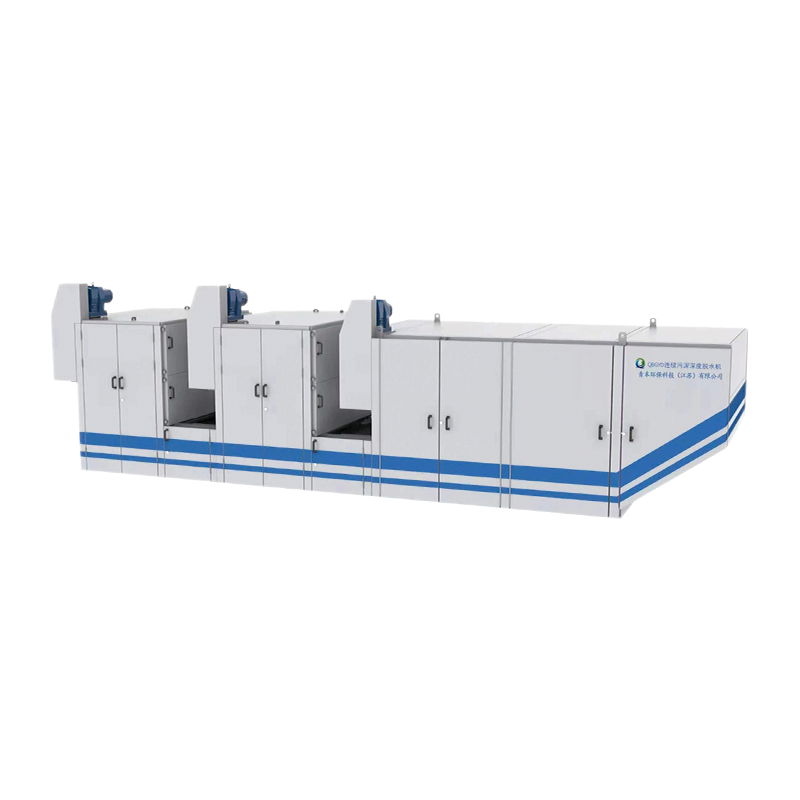
In wastewater treatment and sludge management, sludge drying is a crucial step in reducing volume, lowering transportation costs, and enabling resource recovery. Traditional high-temperature drying systems are widely used due to their fast drying speed, but low-temperature sludge drying systems have recently gained increasing attention.
This article will compare low-temperature and high-temperature drying in terms of efficiency, energy consumption, environmental impact, and sludge properties, helping users in the industrial and environmental protection fields choose the most suitable sludge drying method.
1. Impact of Drying Temperature on Sludge Properties
High-Temperature Drying
High-temperature drying generally refers to drying temperatures above 150°C. Its advantages include fast drying speed and significant reduction in sludge moisture content, making it suitable for situations requiring rapid processing of large amounts of sludge. However, high temperatures can lead to the following problems:
Increased decomposition of organic matter: Some organic matter is destroyed, affecting the fertilizer value of the sludge.
Increased odor and harmful gas emissions: High temperatures easily produce malodorous gases and harmful volatile substances, requiring supporting gas treatment equipment.
High energy consumption: High-temperature heating requires a large amount of energy, resulting in higher operating costs.
Low-Temperature Drying
Low-temperature drying generally refers to drying temperatures below 100°C, exemplified by low-temperature sludge drying systems. Advantages include:
Preservation of organic matter: Low-temperature drying can maximize the preservation of organic matter and microbial activity in the sludge, facilitating subsequent resource utilization.
Reduced odor and harmful emissions: Due to the lower temperature, there is less decomposition of organic matter, significantly reducing odor and harmful gas emissions.
Energy saving and environmental protection: Compared to high-temperature drying, low-temperature systems generally consume less energy and are more suitable for long-term operation.
2. Comparison of Drying Efficiency
High-temperature drying is fast, generally reducing sludge moisture content from 70%-80% to 10%-20% within a few hours. Low-temperature drying systems, due to the lower temperature, require a relatively longer drying time, taking several days or utilizing continuous low-temperature drying technology.
However, with technological advancements, modern low-temperature sludge drying systems have significantly improved drying efficiency through:
Heat pump drying
Waste heat recovery
Continuous flow drying equipment
while maintaining the advantages of low-temperature drying.
3. Environmental and Operating Cost Considerations
In the context of increasingly stringent environmental regulations, low-temperature drying systems offer significant advantages:
Reduced odor and pollutant emissions, meeting emission standards
Low energy consumption, reducing operating costs
Although high-temperature drying is faster, it requires more energy and a complementary gas treatment system, resulting in higher operating complexity and costs.
Therefore, for environmentally friendly sludge treatment plants or long-term operating projects, low-temperature sludge drying systems are a more economical and environmentally sound choice.
4. Sludge Resource Utilization Potential
The dried sludge can be used for:
Producing organic fertilizer
As biomass fuel
Soil conditioner
High-temperature drying destroys some organic matter and nutrients, reducing its reuse value. Low-temperature drying preserves the organic matter and microbial activity of the sludge, making it more suitable for resource utilization and recycling.

5. Summary of Applicable Scenarios
| Drying Method | Applicable Scenario | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High-Temperature Drying | Large-scale industrial sludge rapid processing | Fast drying, small footprint | High energy consumption, loss of organic matter, difficult to control emissions |
| Low-Temperature Drying | Environmentally friendly sludge treatment plants, resource recovery projects | Energy-saving, environmentally friendly, preserves organic matter, easier to meet emission standards | Longer drying time, higher equipment investment |