In the process of urban sewage and sludge treatment, sludge treatment has always been a thorny and important issue. With the increase in population and the acceleration of industrialization, sewage treatment plants process a large amount of sewage every day, and the sludge accumulates gradually as the water is purified. Therefore, the method of sludge treatment has become a key link in sewage treatment. Sludge drying and incineration are two common treatment methods. So, what is the difference between sludge drying and sludge incineration?
1. Sludge Drying: Efficiently Reducing Sludge Volume
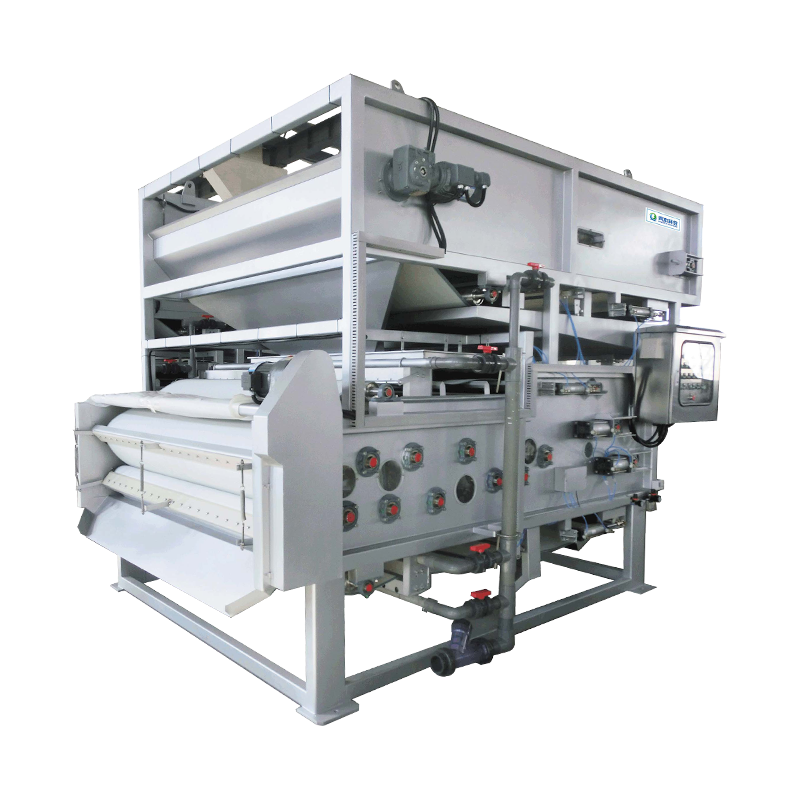
Sludge drying is a treatment method that reduces the volume of sludge by evaporating water. It mainly uses physical methods, utilizing heat sources (such as solar energy, hot air, hot water, or electric heating, etc.) to heat the sludge, causing the water to evaporate, thereby reducing the moisture content of the sludge to a more ideal level. Dried sludge has a lower moisture content than raw sludge, reducing its transportation and disposal costs.
(1) Drying Process
In the sludge drying process, the evaporation of water is the main mechanism. Common drying equipment includes belt dryers, rotary dryers, and fluidized bed dryers. Through these devices, the water in the sludge can be evaporated, so that the final moisture content of the sludge is reduced to below 50%. The volume of the dried sludge is greatly reduced, making it easier to transport, store, and ultimately dispose of.
(2) Advantages
The advantages of sludge drying are that the treatment process is relatively simple, the equipment is mature, and it can greatly reduce the volume of sludge, reducing the difficulty of subsequent treatment. In addition, dried sludge is less likely to produce foul odors, is more environmentally friendly, and helps reduce pollution to the surrounding environment. Dried sludge can be used as a soil conditioner or fertilizer, and has certain resource utilization value.

(3) Disadvantages
Although sludge drying has many advantages, it also has some shortcomings. First, the drying process requires a large amount of energy, especially thermal energy, which increases the cost of sludge treatment. Secondly, the dried sludge still contains certain harmful substances and cannot completely avoid potential environmental pollution.
2. Sludge Incineration: Complete Elimination of Sludge and Power Generation
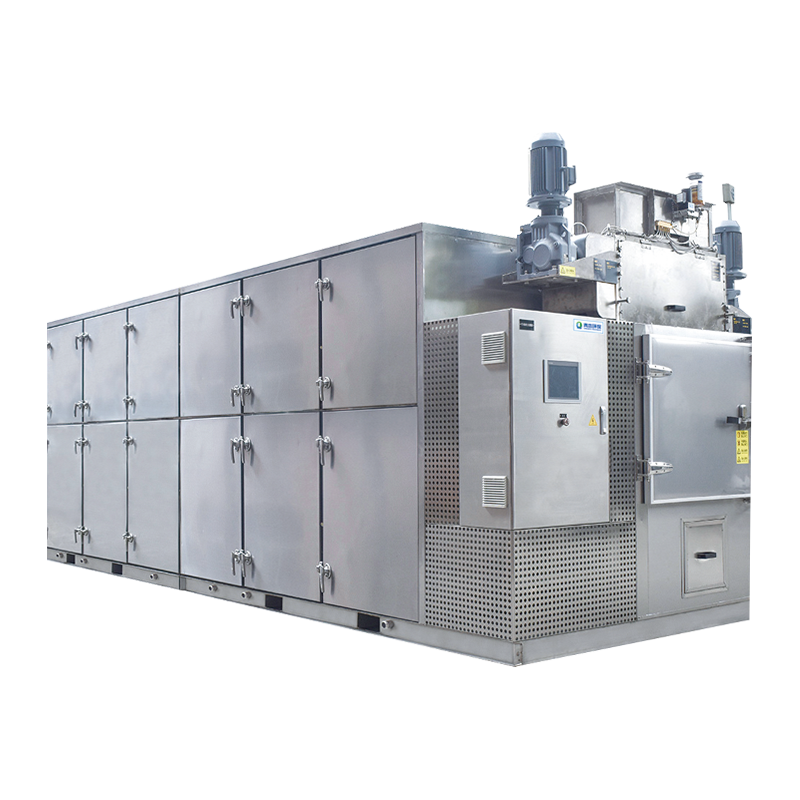
Sludge incineration involves burning sludge at high temperatures to completely eliminate its volume. The incineration process not only significantly reduces the volume of sludge but also effectively eliminates harmful substances, especially pathogenic microorganisms and toxic substances. The residue after incineration is mainly ash, and the heat generated can be used for power generation or other energy utilization.
(1) Incineration Process
Sludge incineration is usually carried out in specialized incinerators. After pretreatment, the sludge is processed through high-temperature incineration (usually between 800-1000°C). During the incineration process, the organic matter in the sludge is completely oxidized into carbon dioxide, water, and a small amount of ash. The final product of incineration is mainly ash, which usually requires further disposal.
(2) Advantages
The biggest advantage of sludge incineration is its ability to achieve complete elimination of sludge. The ash produced after incineration has a small volume, facilitating final disposal. During the incineration process, harmful substances and pathogenic microorganisms in the sludge are completely destroyed, greatly reducing environmental pollution. In addition, the heat generated during the incineration process can be used for power generation or heating, achieving energy recovery and reuse.
(3) Disadvantages
The disadvantages of sludge incineration are that it requires high temperatures and a large amount of energy, making the cost of incineration relatively high. Furthermore, the incineration process may produce some harmful gases, such as dioxins and nitrogen oxides, which can affect air quality if not properly treated. Therefore, incineration equipment must be equipped with efficient exhaust gas treatment facilities to ensure that the incineration process does not cause secondary pollution to the environment.
3. Comparison of Sludge Drying and Sludge Incineration
From the above discussion, we can see that sludge drying and sludge incineration have significant differences in several aspects. The following is a comparison of them in several key indicators:
| Feature | Sludge Drying | Sludge Incineration |
| Treatment Principle | Reduces sludge volume by evaporating water | Eliminates sludge through high-temperature combustion and destroys harmful substances |
| Post-treatment Products | Reduced sludge volume, still contains harmful substances | Main product is ash, harmful substances are completely destroyed |
| Energy Consumption | Requires a large amount of thermal energy, high energy consumption | High-temperature incineration process requires significant energy, high cost |
| Water Quality Protection | Evaporation of water, but cannot completely eliminate harmful substances | Completely destroys harmful substances, ensuring better water quality protection |
| Environmental Impact | Relatively eco-friendly, but equipment needs regular cleaning | If waste gas is not treated properly, harmful gases may be emitted |
| Resource Utilization | Dried sludge can be used for soil improvement or fertilizer | Ash from incineration can be used in building materials or other resources |
| Applicable Scenarios | Suitable for treating low to medium concentration sludge | Suitable for large-scale sludge treatment and high-concentration sludge |

4. Selecting Appropriate Sludge and Wastewater Treatment Equipment
In practical applications, the choice of sludge dewatering or sludge incineration as part of wastewater treatment should be determined based on the actual situation. Sludge dewatering is suitable for situations with smaller sludge volumes or where sludge recycling is required, while sludge incineration is more suitable for treating large volumes of sludge and where complete elimination of harmful substances is necessary. Typically, wastewater treatment plants select appropriate sludge treatment technologies based on the nature of the sludge, treatment capacity, budget, and environmental requirements.